A sight glass is a simple but important device that allows operators to visually check the liquid condition inside equipment or piping.
In chemical plants—especially batch processes—sight glasses are widely used except in extremely high-pressure or high-temperature services.
Although instruments such as conductivity meters or density sensors are available, visual confirmation by human operators still plays a critical role, particularly in separation and quality control processes.
This article explains the main types of sight glasses and how to use them correctly, from an operational and design perspective.
The Role of Sight Glasses in Chemical Plants
The main purpose of a sight glass is to provide direct visual information that instruments alone cannot fully replace.
In operations such as liquid–liquid separation, operators often need to judge:
- Phase boundaries
- Intermediate layers
- Changes in appearance
For these tasks, sight glasses remain an essential part of the process.
Choosing the right type of sight glass is important not only for visibility, but also for quality stability and safety.
Lantern-Type Sight Glass
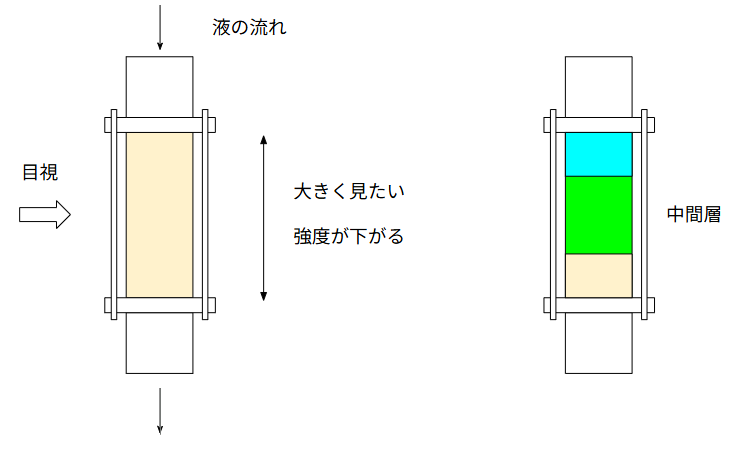
Among various sight glasses, the lantern-type sight glass is the most important for daily plant operation.
It has a cylindrical shape, which provides a wide viewing area.
Compared to cross-type sight glasses, the visibility is significantly better.
Why Lantern-Type Sight Glasses Are Important for Quality
Lantern-type sight glasses are especially useful for liquid–liquid separation.
During separation, there are usually:
- An upper layer
- A lower layer
- An intermediate layer between them
The amount and handling of the intermediate layer depend on the process.
When the interface is unclear, a wide viewing range helps operators distinguish layers accurately, reducing separation failures and stabilizing product quality.
Although instruments such as conductivity meters or density meters can assist, human visual judgment is still required in many cases.
Design Considerations
Operators prefer longer cylindrical sections for better visibility.
However, a longer glass section results in lower mechanical strength.
From a design standpoint:
- External loads on the sight glass should be minimized
- Piping and equipment should be designed to reduce stress
If a lantern-type sight glass breaks, all contained hazardous liquid may be released, making proper design and placement critical.
Cross-Type Sight Glass
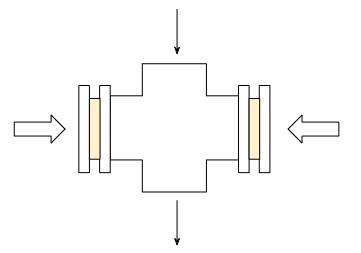
A cross-type sight glass consists of a small circular glass disk installed at the end of a cross fitting.
Because the glass area is small, mechanical strength is high.
However, the viewing area is limited, so it is not suitable for frequent operational monitoring.
Typical Applications
Cross-type sight glasses are commonly used when:
- Only the presence or absence of liquid needs to be confirmed
- Visual inspection is required under high-pressure conditions
In processes without liquid–liquid separation, a plant may be designed using only cross-type sight glasses.
In general, they are more common in plants with lower quality sensitivity.
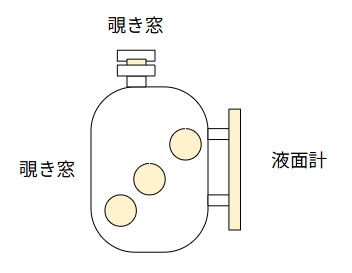
Level Gauge Type (Sight Glass Level Indicator)
Level gauge types are often categorized as level indicators rather than simple sight glasses.
Typical examples include reflex-type level gauges installed on tanks.
For small tanks, a single gauge may be sufficient.
For large tanks or columns, multiple level gauges are often required by regulations, such as fire safety laws.
Practical Usage
In batch operations, manual sight glass level gauges are rarely used for large tanks.
Instead, instrument-based level transmitters are commonly adopted.
Sight glass level indicators are mainly used in:
- Continuous separation systems
- Applications where confirming a stable liquid level is necessary
Tank viewing windows are sometimes considered sight glasses, but functionally they are similar to cross-type sight glasses used only for visual confirmation.
Conclusion
Sight glasses serve different purposes depending on their type.
- Lantern-type: Essential for separation and quality-critical operations
- Cross-type: Suitable for high-pressure areas and simple liquid presence checks
- Level gauge type: Used mainly for continuous operation and level confirmation
Rather than installing sight glasses simply because “you can see inside,”
it is important to select them based on what needs to be confirmed and how much human judgment is required.
Proper selection improves both process safety and product quality.

Comments