Handling powders inside a hopper always carries a dust-explosion risk.
Both filling and discharging operations can unintentionally create the perfect combination of oxygen, a combustible powder cloud, and ignition sources such as static electricity.
This article explains practical dust-explosion countermeasures specifically for powder hoppers in chemical plants—focusing on inerting with nitrogen, sealing the filling point, grounding, and preventing blockage at the discharge. The content is based on real plant-engineering practice and is written for beginners who want an accurate, operation-ready design guideline.
1. Countermeasures During Filling
1.1 Use an Inert Atmosphere (Nitrogen Purging)
During powder filling, air can easily enter the hopper, especially when unloading from flexible containers (FIBCs).
If this open space mixes powder and oxygen, an ignitable atmosphere can form.
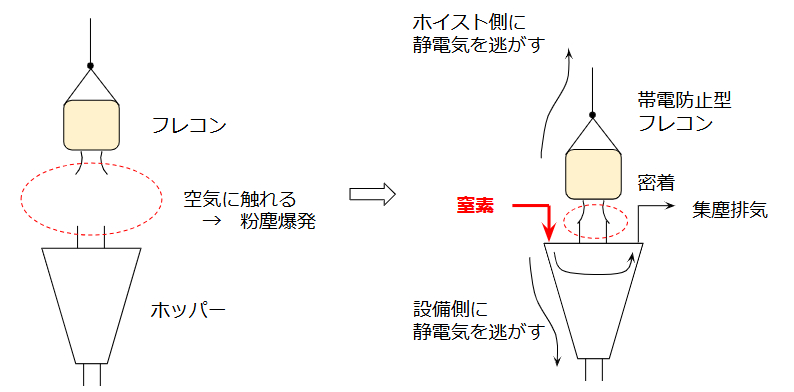
To prevent this, hoppers should be handled under a nitrogen atmosphere:
- Install a nitrogen nozzle on the top section of the hopper.
This ensures stable N₂ flow even when powder accumulates. - The exhaust usually flows into the existing dust-collection duct, so no special vent system is required.
A top-mounted nitrogen inlet is preferred because bottom inlets can become ineffective as the powder level rises.
1.2 Seal the Filling Connection
An open FIBC–hopper interface allows air ingress and increases dust dispersion.
A closed or sealed connection structure significantly reduces ignition risk.
Keeping external air out is one of the simplest and most effective explosion-prevention measures.
1.3 Manage Static Electricity
Powders generate static charge through friction.
Both the container and hopper must be designed to safely discharge static electricity:
- Use static-dissipative FIBCs (Type B, C, or D).
- Metal drums must be properly grounded—but grounding mistakes are common.
- Hoppers usually have inherent grounding through the structure, but the connection should still be confirmed.
In practice, FIBCs often offer more reliable grounding because the hoist system forces an electrical connection.
2. Countermeasures During Discharge
2.1 Prevent Blockage at the Narrow Outlet
Because hoppers taper downward, the discharge area is prone to bridging or ratholing.
If blockage occurs, operators might consider air blow.
However, for dust-explosion safety:
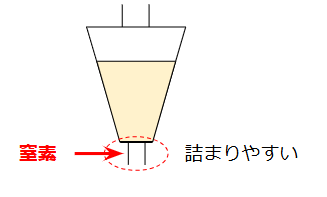
👉 Air blowing must be replaced with nitrogen blowing.
Design notes:
- Install a nitrogen blow nozzle directly at the narrowed discharge section.
- Do not extend the blow pipe deep inside the discharge nozzle—it can worsen blockage.
2.2 Continue Nitrogen and Static Control to the Downstream Equipment
Explosion prevention does not end at the hopper.
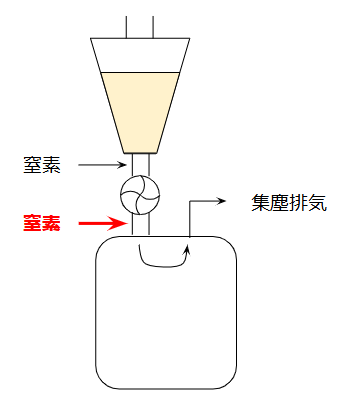
The powder continues into a downstream reactor, mixer, or conveyor, so the entire line must maintain safe conditions:
- Add a nitrogen line below the discharge valve.
- Nitrogen naturally flows toward the equipment’s exhaust system.
- Adding N₂ at the top nozzle of the equipment can cause powder blockage; the piping line is usually a better place to interface nitrogen.
Many processing units have limited nozzles, so designing the nitrogen line from the piping side is often the practical approach.
Conclusion
Powder hoppers present different dust-explosion risks during filling and discharging.
However, the main hazards—oxygen, static electricity, and blockage—are consistent across both steps.
Effective engineering controls include:
- Filling: sealed connection, nitrogen inerting, static-dissipative equipment
- Discharging: nitrogen blowing at the outlet, continued grounding and inerting into downstream equipment
By integrating these into the design and operation of powder hoppers, chemical plants can significantly reduce dust-explosion risks.
About the Author – NEONEEET
A user‑side chemical plant engineer with 20+ years of end‑to‑end experience across design → production → maintenance → corporate planning. Sharing practical, experience‑based knowledge from real batch‑plant operations. → View full profile

Comments